Dehydrogenation Catalyst
Dehydrogenation Catalyst
- High Temperature Dehydrogenation Catalytic Technology
Such as iron oxide – chromium oxide – potassium oxide can make ethylbenzene (or n-butene) dehydrogenation into styrene (or butadiene) under high temperature and a large amount of water vapor.
- low temperature dehydrogenation catalytic technology
Because dehydrogenation generally needs to be carried out at high temperature, decompression or in the presence of a large number of diluents, the energy consumption is large. In recent years, oxidative dehydrogenation at lower temperatures has been developed. Such as polyethylene with bismuth – molybdenum metal oxide catalyst by oxidative dehydrogenation of butadiene.
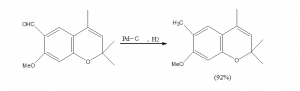
Hydrogenation catalyst is not only used in the production process, but also widely used in the refining process of raw materials and products. According to different hydrogenation conditions, it can be divided into three categories:
① Selective hydrogenation catalysts, such as ethylene and propylene obtained from petroleum hydrocarbon cracking as polymerization raw materials, must first be selected by hydrogenation, to remove trace impurities such as alkyne, diene, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, oxygen, and no loss of ene. The catalyst used is generally palladium, platinum or nickel, cobalt, molybdenum, etc., on alumina.
② Non-selective hydrogenation catalyst, that is, the catalyst used for deep hydrogenation to saturated compounds. Such as benzene hydrogenation to cyclohexane with nickel-alumina catalyst, phenol hydrogenation to cyclohexanol, has dinitrile hydrogenation to hexdiamine with nickel catalyst.
③ Hydrogenation catalyst, such as copper chromate catalyst for oil hydrogenation to produce higher alcohols
It is the earliest complexation catalyst used in industrial production. Aldehydes with one more carbon atom are produced by the reaction of alkenes with syngas (CO+H2) in the presence of catalyst. Such as ethylene, propylene as raw materials through hydroformylation (that is, known as carbonyl synthesis) propyl aldehyde, butyl aldehyde. Hydroformylation was carried out in the liquid phase at high temperature and pressure using carbonyl cobalt complex as catalyst.
Polyethylene is mainly divided into low density and high density. In the past, the former used high pressure method (100 ~ 300MPa) production, oxygen, organic peroxide as catalyst. The latter is mainly produced by medium pressure method or low pressure method. In medium pressure method, chromium-molybdenum oxide is carried on silicon aluminum glue as catalyst. In low pressure method, Ziegler type catalyst (represented by titanium tetrachloride and triethyl aluminum system) is used for polymerization at low temperature and low pressure. Polypropylene production also developed supported titanium-aluminum system of high efficiency catalyst, per gram of titanium can produce more than 1000kg of polypropylene.
It is the earliest complexation catalyst used in industrial production. Aldehydes with one more carbon atom are produced by the reaction of alkenes with syngas (CO+H2) in the presence of catalyst. Such as ethylene, propylene as raw materials through hydroformylation (that is, known as carbonyl synthesis) propyl aldehyde, butyl aldehyde. Hydroformylation was carried out in the liquid phase at high temperature and pressure using carbonyl cobalt complex as catalyst.
Write your message here and send it to us